Intelligent Data and Threat Analytics
Enhancing data quality, diversity, and resilience to improve the reliability of AI-driven detection systems. Addresses data imbalance, poisoning resistance, and representation learning to strengthen next-generation cyber defense capabilities.
Data-centric AI | Intrusion detection | Synthetic data generation | Adversarial robustness | Explainable security models
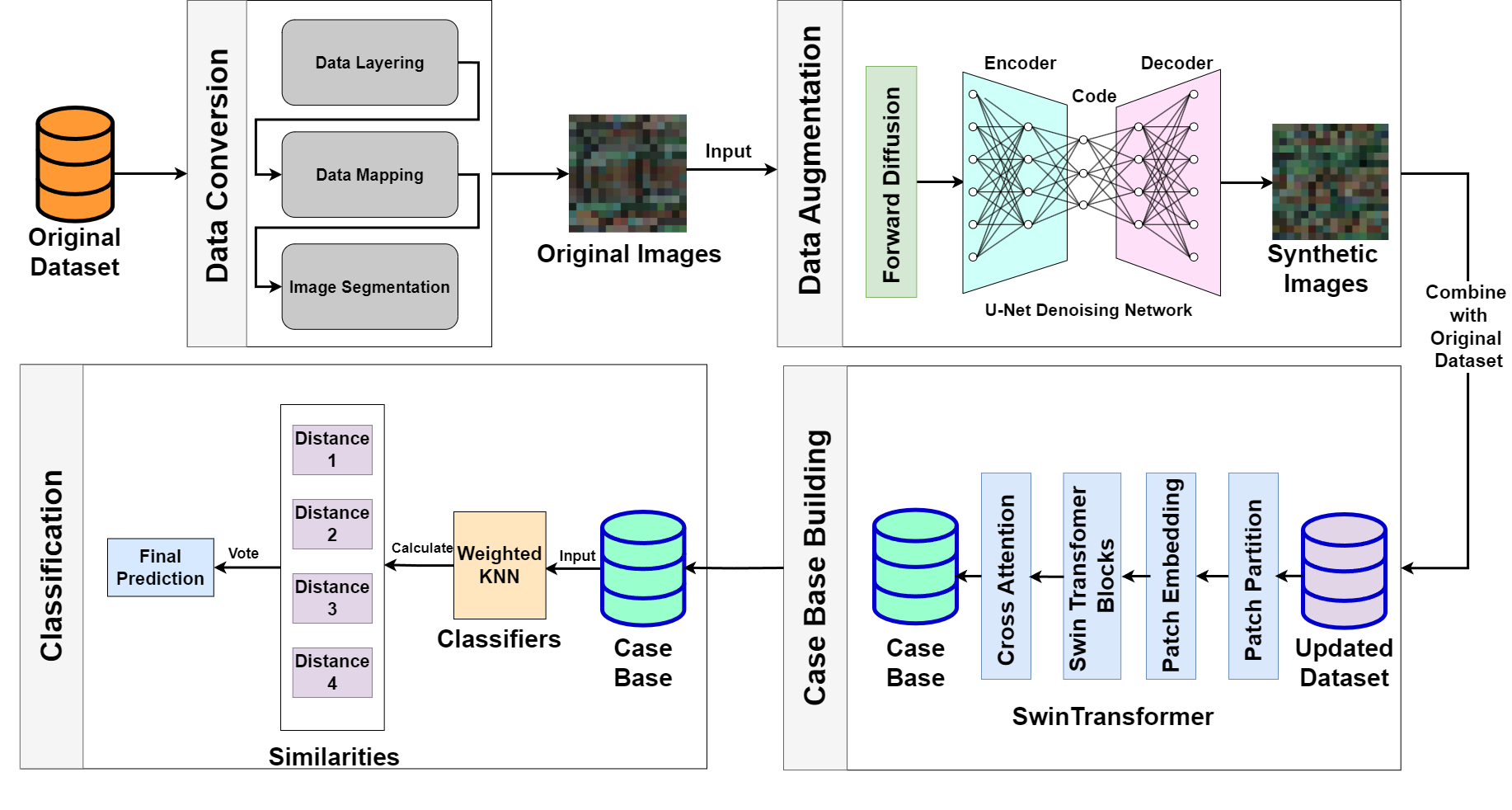
Case-Based Reasoning with Diffusion Model for Ransomware Detection
- Project URL: Click here
In recent years, the threat and damage caused by ransomware have been steadily increasing. Although many detection methods have been proposed, network security remains a severe challenge due to the continuous emergence of new attack techniques, data imbalance, low detection rates of existing methods, and the lack of interpretability in model decision-making. This study proposes a Case-Based Reasoning with Diffusion Model for Ransomware Detection (CBR-DRD), which classifies network traffic information without feature loss or redundancy by converting it into RGB images. The dataset is then augmented using image generation based on a U-Net diffusion model. Features extracted by a Swin Transformer are used to construct a case base, and a weighted K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) algorithm is employed to classify the traffic by computing the similarity between a given sample and existing cases, to determine whether it is associated with ransomware activity. Compared with two similar ransomware detection approaches and commonly used generative models, namely the GAN model and a ResNet-based diffusion model designed to address data imbalance, the proposed method achieves superior performance on both the USTC-TFC2016 and ISOT datasets.
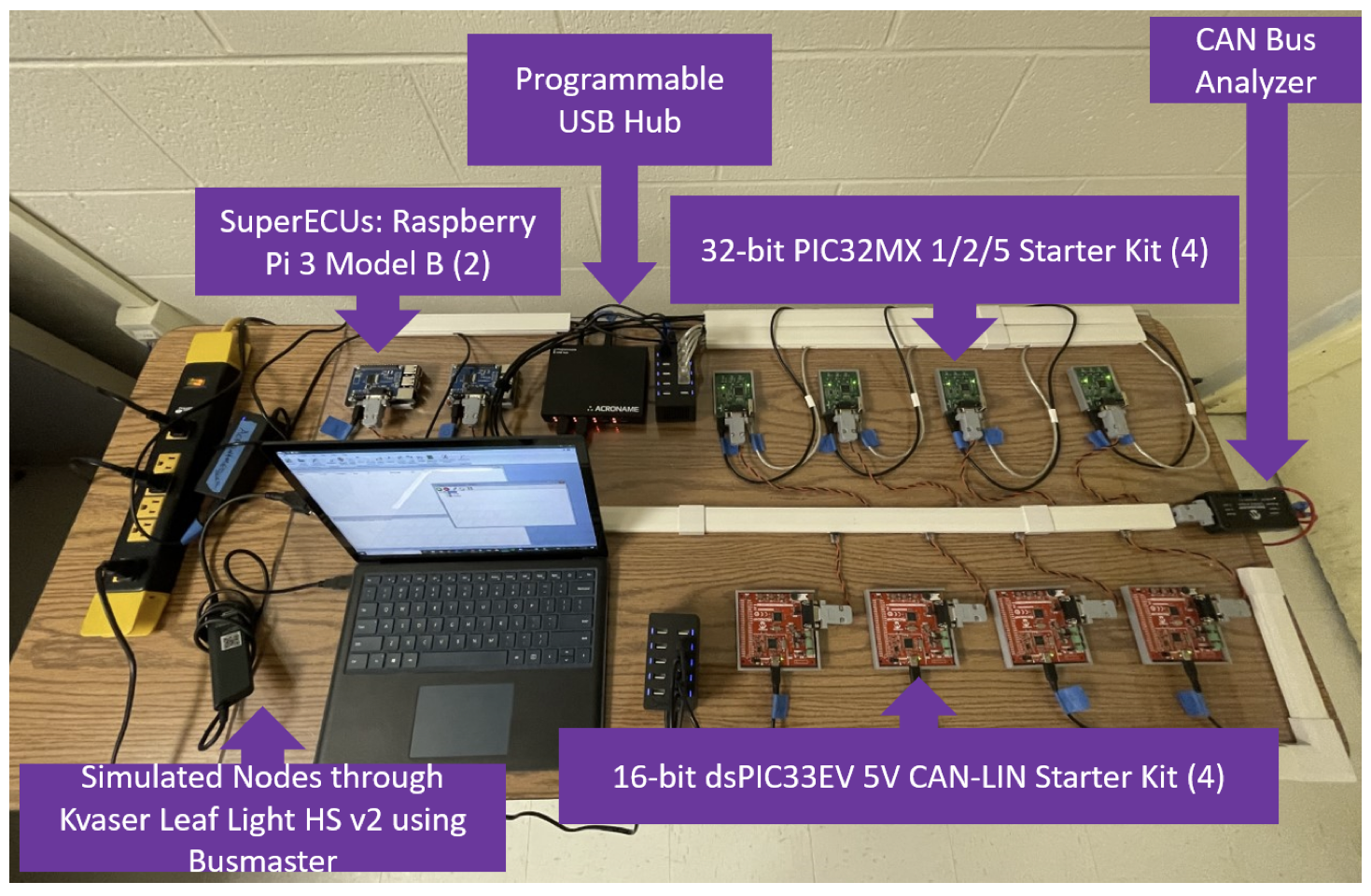
Design and Development of XiveNet: A Hybrid CAN Research Testbed
- Project URL: Click here
We have developed an affordable distributed Internet of Things (IoT) testbed, named XiveNet, to conduct in-vehicle security research. This testbed merges the adaptability of simulators with the real-time ECU characteristics of actual vehicles. The testbed is made up of ECU chips found in vehicles, Raspberry Pis, and is combined with a bus master simulator. Our experiments with CAN (controller area network) traffic from actual vehicles (Oak Ridge National Laboratories Road Data Set) demonstrate that our testbed closely replicates the attributes of a real vehicle. We have further authenticated our testbed by deploying SecCAN, a secure CAN algorithm, and evaluating its security by injecting invalid frames. Furthermore, we examined ORNL’s timing-based intrusion detection on our testbed and successfully produced alerts. Additionally, we incorporated Named Data Networking (NDN) capable nodes, providing researchers with an additional resource to develop future in-vehicle security solutions. Finally, we have proposed a bitrate hopping technique focused on preventing the denial of service attack and conducted a preliminary investigation using the testbed. Our evaluation and validation indicate that the testbed provides the real-world vehicle environment with the flexibility of a simulation environment that supports a wide range of hardware and software configurations.
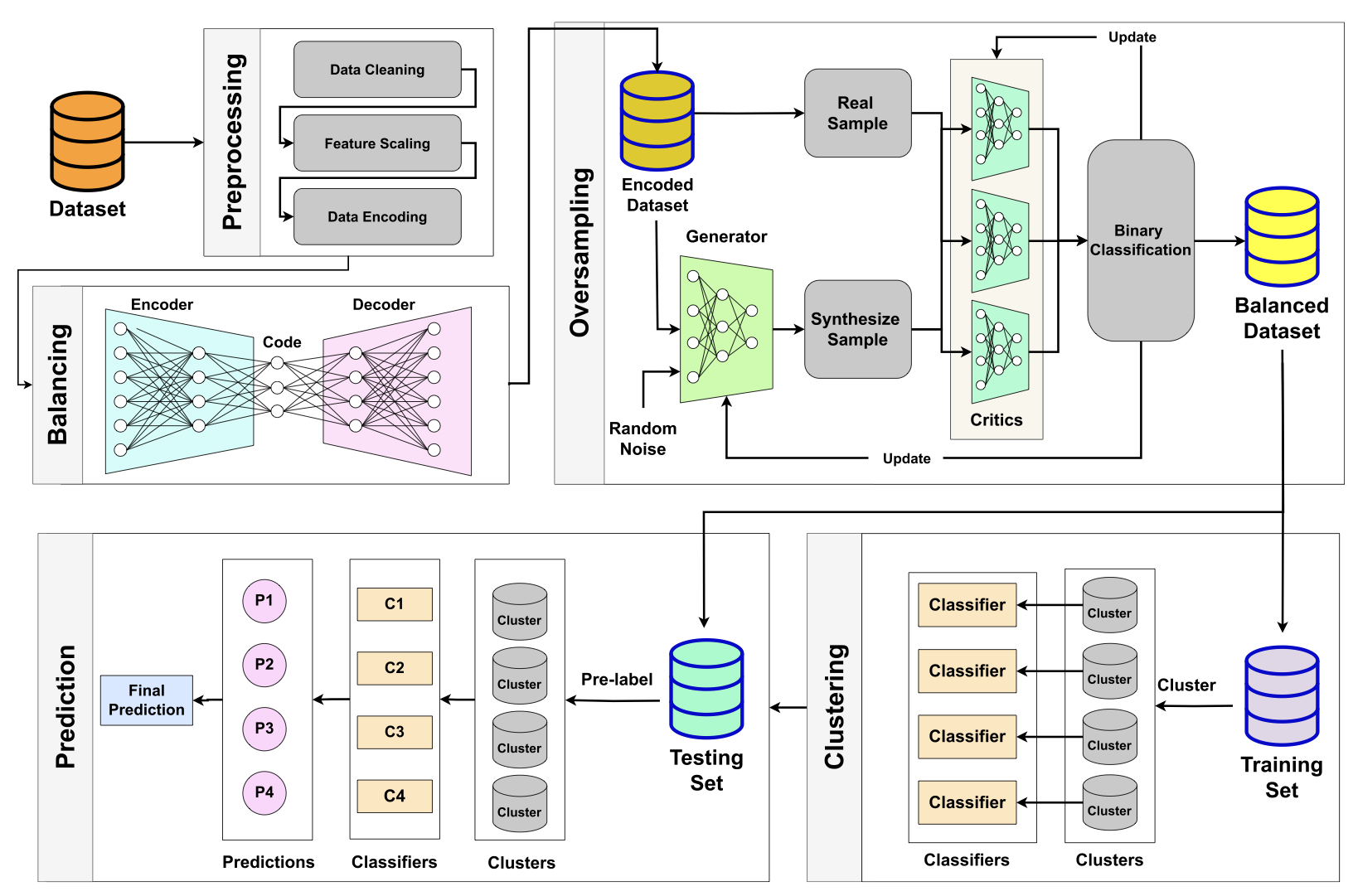
Clustering-Based Intrusion Detection System Meets Multicritics Generative Adversarial Networks
- Project URL: Click here
Network security has continuously been a major focus of research and concern on a global scale. The intrusion detection system (IDS), as a crucial defensive measure against network attacks, has undergone multiple iterations and evolutions since its inception to adapt to the ever-changing network environment. Due to the widespread issue of data imbalance in network security datasets, a single machine learning or deep learning model often struggles to effectively handle different types of attacks. In this work, we propose a multicritics generative adversarial networks (GAN) clustering-based IDS (MCGC-IDS) model to address the issue of data imbalance. The quality of the generated data is analyzed using correlation heatmaps and PCA plots, which later is used to update the dataset that is utilized for feature extraction with autoencoders (AEs). Subsequently, CNN-LSTM models are employed to analyze clusters formed by the weighted fuzzy c-means (WFCM) clustering algorithm to achieve enhanced performance for the IDS system. This model is then compared with two existing models. The results indicate that while the GAN-generated data retains the original dataset distribution, it also addresses the issue of imbalance. Moreover, the subsequent multilayered processing enables the overall model to more effectively handle various types of attacks. Finally, when this model is tested on a similar dataset, the UNSW-NB15, it continues to demonstrate superior performance, indicating its strong generalizability.