Trust, Privacy, and Identity in IoT Systems
Developing scalable frameworks that ensure trustworthiness, authentication, and privacy protection across IoT ecosystem. Integrate trust propagation, device fingerprinting, and privacy-preserving supporting secure interactions between interconnected devices.
IoT trust modeling | Zero-trust | Privacy-preserving data exchange | Traffic-based device profiling | AI-based Traffic obfuscation
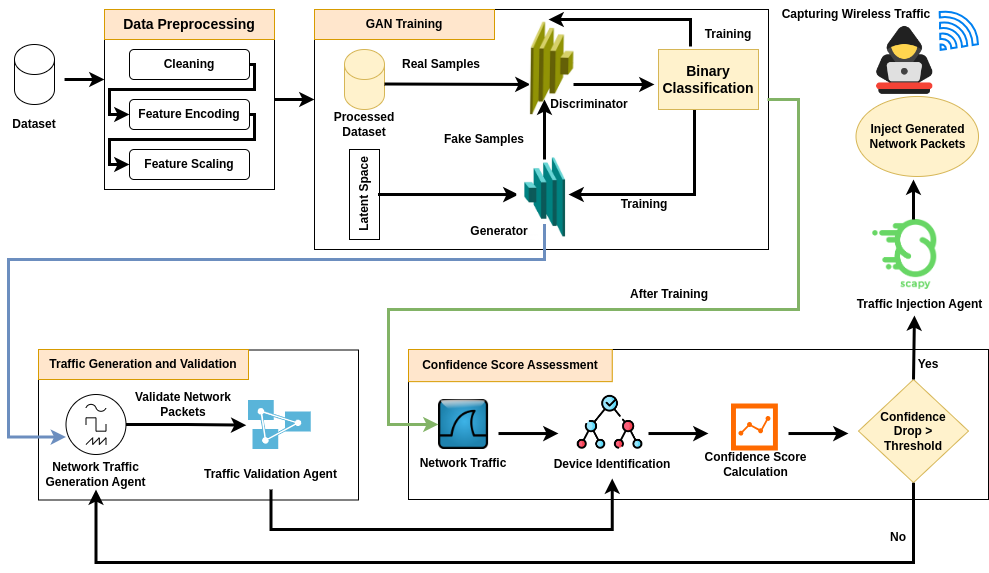
A Dynamic GAN-Based Obfuscation Approach Against Profiling Attacks
- Project URL: Click here
The rapid growth in the number of wireless IoT devices has introduced new privacy challenges. Adversaries can exploit captured wireless traffic to profile and identify specific devices within the network. While several device identification frameworks have been developed to classify and identify devices, researchers have proposed methods such as traffic padding, shaping, and cover traffic injection to counteract identification attempts. However, these approaches often prove ineffective when adversaries gain access to the network. In this study, we propose a GAN-based traffic generation and injection framework designed to enhance device privacy against traffic analysis attacks, even in the presence of local adversaries. Our approach generates highly realistic network traffic and achieves a 98.5% success rate in seamlessly injecting packets into the network without any observable issues. By reducing the prediction confidence of multiple device identification approaches in predicting the origin of network traffic, our framework effectively enhances the privacy of IoT devices. Furthermore, the proposed solution incurs minimal performance overhead, making it a practical and efficient approach to addressing the growing privacy challenges in wireless networks.
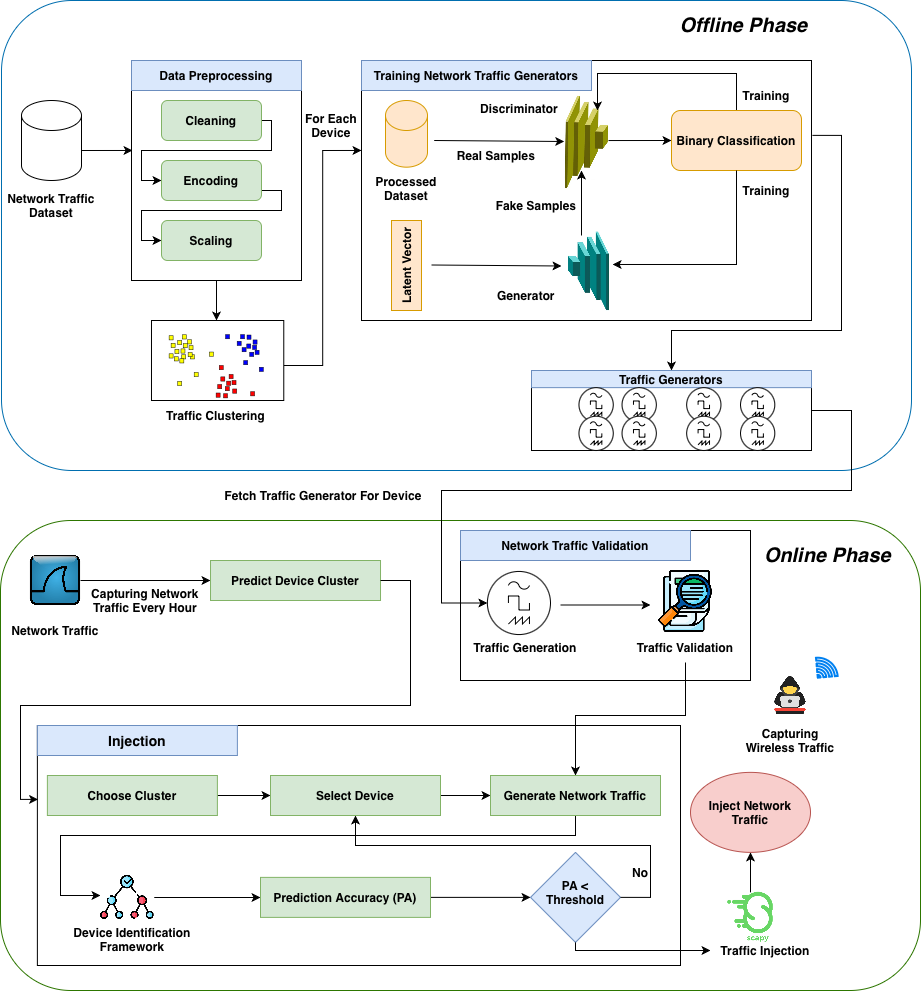
GANFUSION: GAN-Fused Synthetic Injection for Obfuscating Network Traffic Analysis
- Project URL: Click here
Wireless networks have enhanced communication by making it seamless and accessible, however, they have introduced significant privacy vulnerabilities. Adversaries can passively monitor and analyze network traffic to identify devices and user activities. While traditional identifiers such as IP and MAC addresses can be easily spoofed, machine-learning approaches leverage traffic characteristics like packet sizes, timing, and protocol usage to fingerprint devices with high accuracy. This capability threatens user privacy by exposing sensitive behavioral patterns and personal habits. Although several countermeasures such as traffic padding, shaping, and cover traffic injection have been proposed to counteract such adversarial profiling their effectiveness remains limited, particularly against internal adversaries with full network visibility. In this study, we propose GANFUSION, a GAN-based traffic generation and injection framework designed to confuse machine learning classifiers. By emulating diverse device behaviors, GANFUSION masks genuine traffic patterns, making accurate identification more difficult for adversaries. Experimental results demonstrate that GANFUSION significantly reduces device identification accuracy and classifier confidence across all devices, outperforming existing countermeasures. It maintains 99.6% packet correctness while introducing only 83 bytes of bandwidth overhead, making it both effective and efficient for real-world privacy protection. Furthermore, it intelligently selects specific devices to increase uncertainty in classification outputs, enhancing resistance against network-based profiling attacks.
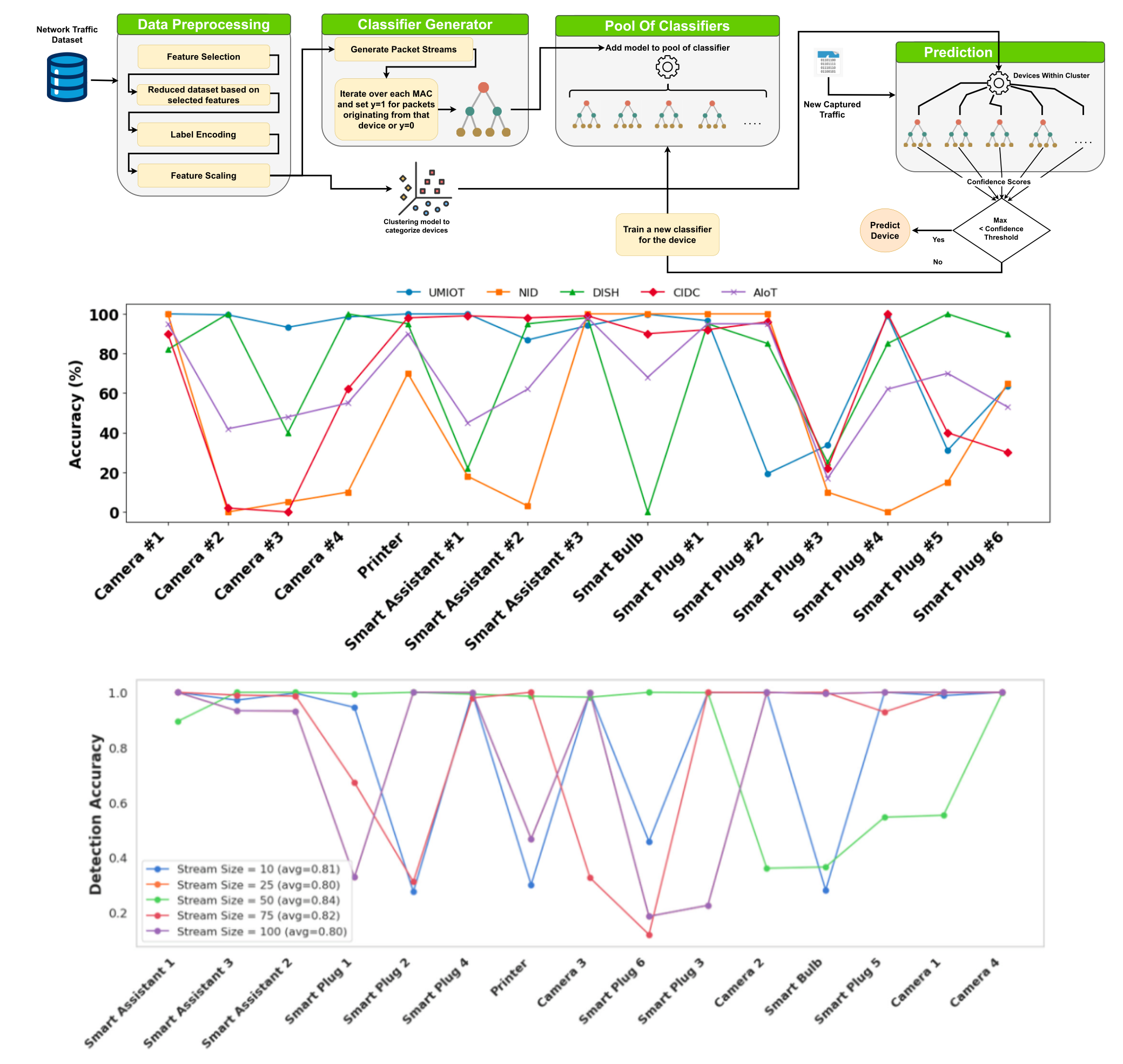
Unmasking IoT Devices: A Dynamic and Adaptive Classification Approach
- Project URL: Click here
The proliferation of IoT devices has revolutionized automation and connectivity across various industries. These devices rely extensively on wireless communication, enabling flexibility and real-time data exchange. The unique traffic patterns they produce, shaped by protocol usage, communication frequency, and data exchange behaviors allow for accurate device identification-based solely on network activity. Previous research on IoT device identification has shown promise but faces key limitations including scalability, requiring frequent retraining for new devices, and are computationally intensive and unsuitable for real-time use. Reliance on spoofable attributes like IP and MAC addresses, or documentation-based profiling, further reduces reliability. To overcome these limitations, this study introduces UMIoT, an adaptive and dynamic multi-classifier framework for IoT device identification. UMIoT is trained on packet-streams, assigns a dedicated classifier to each device, improving accuracy, scalability, and adaptability. Furthermore, UMIoT can efficiently detect the presence of new devices without misclassifying their traffic as belonging to existing devices based on a parameterized confidence-threshold metric. Our experimental results demonstrate that UMIoT achieves high identification accuracy, maintains a low prediction time, enables rapid training for new emerging devices in the network, and operates with minimal storage overhead. Additionally, the results highlight the superiority of the proposed framework against existing device identification approaches both in terms of device identification accuracy and performance metrics including prediction time, storage overhead, and new device training time. The framework is also shown to be resilient against adversarial threats including traffic padding, shaping, and MAC address alteration.